Quick Summary
Salesforce deduplication removes or prevents duplicate records that clutter your CRM, skew reporting, and waste sales team time. This guide covers what Salesforce deduplication is, why it matters, and six proven strategies from native Salesforce tools to automated assignment routing that keep your data clean and your teams productive.
Why Duplicate Records Are a Silent CRM Killer
Duplicate records cause reps to contact the same prospect twice, marketing sends duplicate materials, and reports show inflated pipeline numbers.
Research from Experian shows 83% of commercial companies believe revenue is affected by inaccurate data through wasted resources, lost productivity, and communications spend. Duplicates waste time, erode data trust, and damage customer experience.
This Kubaru guide covers five strategies to identify, prevent, and manage duplicate records in Salesforce.
Why Listen to Us
Kubaru has helped 100+ organizations optimize their Salesforce assignment and routing workflows, including Fortune 500 companies like Genesys, Solarwinds, and Paysafe.

With 140+ five-star AppExchange reviews and deep expertise in Salesforce data management, we’ve seen firsthand how duplicate records impact speed-to-lead and conversion rates.
What Is Salesforce Deduplication?
Salesforce deduplication is the process of identifying, preventing, and removing duplicate records in your CRM. What qualifies as a “duplicate” varies by organization. Some define duplicates as records with identical email addresses, while others require matching across multiple fields like name, company, and phone number.
Common duplicate scenarios include:
- Same email address but different names (John Smith vs. J. Smith)
- Same company with different spellings (IBM vs. International Business Machines)
- Same person existing as both a lead and a contact
- Multiple accounts with old and current addresses
Duplicates happen for several reasons: manual data entry errors, multiple data sources feeding Salesforce, API integrations without deduplication logic, imports from external systems like marketing automation platforms or trade show lists, and missing validation rules.
Types of Duplicates
Not all duplicates are created equal. Understanding the difference helps you determine which records to merge and which to preserve.
Unintentional duplicates represent the same entity in the same business context. These are the problematic duplicates that waste time and obscure relationship context. Examples include multiple lead records for the same person with identical email addresses, two account records with the business name spelled differently, or two accounts where one has an old address and another has the current address. These duplicates split relationship history across multiple records, preventing reps from seeing the complete picture.
Intentional duplicates exist for legitimate business reasons. The same person might work at two different companies over time, requiring separate contact records in each account. Your organization might track the same person in different business contexts (as a prospect in one division and a customer in another). These should be preserved but clearly identified using record types or external identifiers.
5 Strategies for Managing Duplicate Records in Salesforce
1. Use Salesforce Native Matching and Duplicate Rules
Salesforce’s native duplicate detection system combines matching rules and duplicate rules to identify and prevent duplicates. Matching rules define the criteria for what constitutes a duplicate, while duplicate rules determine what actions to take when those criteria are met.
How It Works
First, you configure matching rules to define your match criteria. Salesforce offers four standard matching rules out of the box:
- Standard Account Matching Rule: Matches on account name and billing address
- Standard Contact Matching Rule: Matches on email OR first name + last name + mailing address
- Standard Lead Matching Rule: Matches on email OR first name + last name + company
- Standard Person Account Matching Rule: Matches on email OR first name + last name (requires person accounts to be enabled)
You can customize these rules to match your organization’s needs. Match leads on email alone if that’s your unique identifier. Require both email and phone number for accounts where the same person uses multiple email addresses. Choose between exact matching (fields must be identical), fuzzy matching (allows for minor variations like “Street” vs. “St”), or custom Apex code for complex scenarios.
The matching algorithm can be configured to ignore certain words (like “Inc” or “LLC”) and handle case sensitivity. You can also specify which objects to match against. For example, match new leads against both existing leads and contacts to catch duplicates across objects.
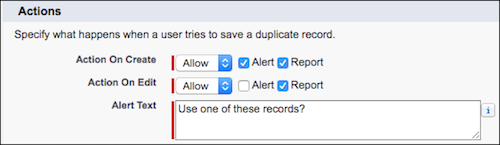
Next, you create duplicate rules that reference these matching rules and define what actions to take. Duplicate rules let you specify conditions for which records should be evaluated and select which matching rules to use. The behavior differs based on how records enter Salesforce:
For manual entry through the UI:
- Allow: Shows a warning but lets the user proceed with creating the duplicate
- Block: Prevents saving the record entirely, forcing the user to merge or cancel
For automated entry via API, imports, or integrations:
- Block only: No warning option exists. The duplicate is rejected.
This creates a critical trap. If you enable blocking for duplicates from your marketing automation platform, trade show imports, or lead enrichment services, you’ll lose valuable data when legitimate duplicates are rejected. These rejections often happen silently, with no notification that records were dropped.
Best For
Organizations of any size can benefit from native Salesforce matching rules, from small teams with fewer than 10,000 records to enterprises adding hundreds or thousands of new records daily. If you have straightforward data structures and work primarily with standard objects, native matching rules provide solid detection without additional cost.
Limitations
Native matching rules scale well and handle high volumes effectively. The limitation is that Salesforce Duplicate Rules don’t automatically merge duplicates. They only alert users or block creation. Every duplicate requires manual review and merging, which doesn’t scale beyond a few dozen duplicates per week. Limited customization compared to third-party tools means you can’t implement sophisticated matching logic or automate merges.
2. Run Duplicate Jobs for Bulk Detection
Duplicate jobs scan your entire existing database to surface duplicates that are already there, not just prevent new ones.
How It Works
When you run a duplicate job, Salesforce creates duplicate record sets—grouped clusters of potential duplicates. Each set contains records that match according to your specified matching rules.
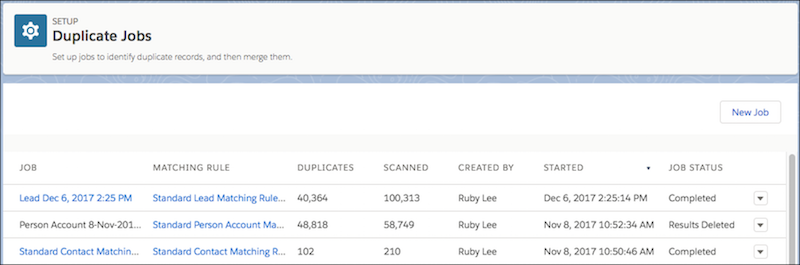
The process:
- Select which object to scan (leads, contacts, accounts, etc.)
- Choose which matching rule to apply
- Salesforce processes your entire database, comparing every record
- Results appear as duplicate record sets you can review
From the duplicate record set view, you can:
- See all records that match
- Compare field values side by side
- Choose which record to keep as the master
- Merge records directly from the interface
The duplicate record sets object is also reportable, enabling you to build dashboards tracking cleanup progress over time. You can see how many duplicate sets exist, which have been resolved, and where the biggest concentrations of duplicates live.
Jobs are processor-intensive and can take hours on large databases. Salesforce also limits how many duplicate jobs can run simultaneously.
Best For
One-time cleanup projects when you’re inheriting messy data or haven’t been actively managing duplicates. Also useful for scheduled maintenance run monthly or quarterly on large databases.
Limitations
Only available in Performance and Unlimited editions. Professional and Enterprise users are locked out, which is frustrating since duplicate problems often hit organizations before they’ve scaled to higher editions. The time-intensive nature means you need to plan carefully, running jobs during off-hours and starting with your highest-priority objects like leads and contacts.
Duplicates must still be reviewed and merged manually. There’s no auto-merging with any standard Salesforce deduplication features.
3. Manual Merging for Quick Fixes
Salesforce’s built-in merge functionality lets you combine up to 3 records at a time for leads, contacts, and accounts.
How It Works
The manual merge process:
- Navigate to one of the duplicate records
- Click “Merge” from the menu
- Search for and select the other duplicate records (up to 2 more)
- Salesforce displays all three records side by side
- Select which record should be the master (survivor)
- For each field, choose which value to keep
- Review and confirm the merge
Related records automatically transfer to the surviving record. Activities, opportunities, cases, and custom object relationships all move over. The non-surviving records are moved to the recycle bin but can be recovered for 15 days if you made a mistake.
You have full control over which data to preserve. If Record A has the correct email but Record B has the correct phone number, you can keep the email from A and the phone from B, with both values living on the surviving record.
Best For
One-off fixes where you’ve discovered a handful of duplicate records. Small cleanups involving fewer than 50 records. Situations requiring manual judgment on which data to preserve, particularly when duplicate records have conflicting information that needs human review.
Limitations
Extremely time-consuming beyond 50 records. If you’re manually merging hundreds or thousands of duplicates, you’re spending hours clicking through merge screens. The process is also prone to human error since you’re making judgment calls on every field for every merge. Not scalable for ongoing maintenance as duplicates continue entering your system.
4. Deploy Third-Party Deduplication Tools
When native Salesforce tools can’t keep pace with your duplicate volume or complexity, third-party deduplication tools become essential.
How It Works
Third-party tools operate both inside and outside Salesforce, depending on the vendor. Most offer:
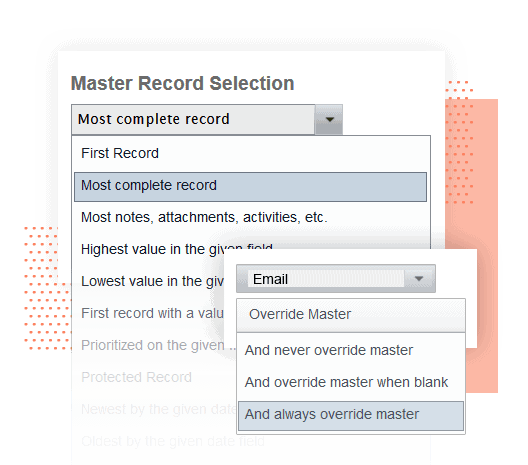
- Automatic duplicate detection: Continuously scan your database using matching algorithms that go beyond Salesforce’s native capabilities. Fuzzy matching catches similar but not identical records (“Robert” vs. “Bob”, “Street” vs. “St”). Some tools use machine learning to improve match accuracy over time.
- Mass merge capabilities: Merge hundreds or thousands of records in bulk instead of three at a time. Define merge rules once, then apply them across entire duplicate sets. Review and approve merges in batches rather than individually.
- Automatic merging: Automatically merge duplicates that meet strict matching criteria (like exact email match) without manual review, while flagging records that meet fuzzy match criteria for human approval.
- Scheduled automation: Set deduplication to run daily, weekly, or monthly. The system identifies new duplicates since the last run and either automatically merges them (based on your rules) or queues them for review.
- Cross-object matching: Match leads against contacts and accounts simultaneously. Identify when the same company appears as both an account and embedded in lead/contact records.
- Integration with Excel and Google Sheets: Export duplicate sets for bulk editing outside Salesforce, then import cleaned data back in.
Popular tools include:
| Tool | Key Strengths | Best For |
| Cloudingo | Visual grid format for side-by-side comparison, strong automation, user-friendly interface | Teams wanting intuitive visual workflows |
| DupeBlocker | Real-time duplicate prevention, works on standard and custom objects, multiple handling options (block, merge, or redirect) | Organizations needing proactive duplicate blocking |
| Plauti Deduplicate | Advanced cross-object matching, field-level restore, Salesforce-native | Complex Salesforce orgs needing sophisticated logic |
| DataGroomr | AI-powered duplicate detection with zero setup, automated cleansing, real-time dashboards | Teams wanting intelligent automation with minimal configuration |
Best For
Mid-market to enterprise organizations processing 100+ new records daily. Teams with complex data structures requiring sophisticated matching logic. Organizations that have let duplicates accumulate and need aggressive cleanup.
Limitations
Additional cost ranging from $1,000 to $10,000+ annually depending on database size and features.
Learning curve to configure matching rules properly. Potential over-reliance on automation if you don’t review results initially. Compare tool cost against the loaded cost of manual hours your team currently spends.
A $2,000 per year tool that saves 10 hours monthly at a $50 per hour loaded rate saves $6,000 annually. Start with sandbox testing to validate your matching criteria, then review automated results for the first few weeks before trusting fully.
5. Route Duplicates to the Same Team Member with Kubaru
Even with robust prevention strategies, duplicates slip through. Standard Salesforce assignment rules distribute records based on territory, lead source, or round robin rotation without accounting for duplicates.
When a duplicate lead or contact enters the system, it often gets assigned to a different rep than the original owner, creating confused customers, territory disputes, and wasted effort. This is especially critical for speed-to-lead, where 78% of customers buy from the first responder.
How It Works
Kubaru ensures duplicates automatically go to the rep who already owns the relationship through two features:
Duplicate Matching Routers
These routers assign duplicate records to the same owner as the existing record by leveraging your Salesforce Duplicate Rules.
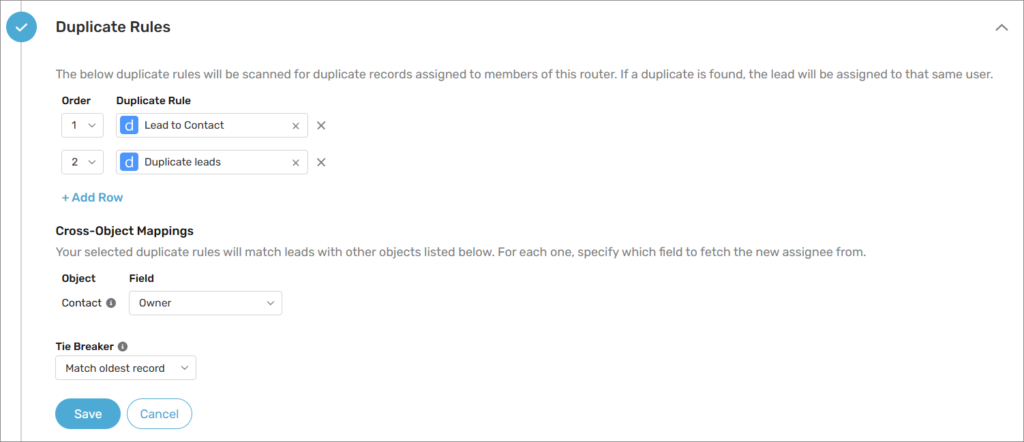
You configure:
- Which Salesforce duplicate rules to reference (use existing matching logic)
- What to do with multiple duplicates (assign to oldest record owner or newest)
When a new record enters Salesforce, Kubaru checks it against your duplicate rules. If a match is found, Kubaru assigns the new record to whoever owns the existing matching record, overriding standard round robin or territory assignment.
Assignment Matching
This feature routes similar records to the same user even when they’re not flagged as official duplicates by Salesforce.
Common use cases:
- Two leads with the same email address go to the same rep
- Multiple contacts from the same company go to the account owner
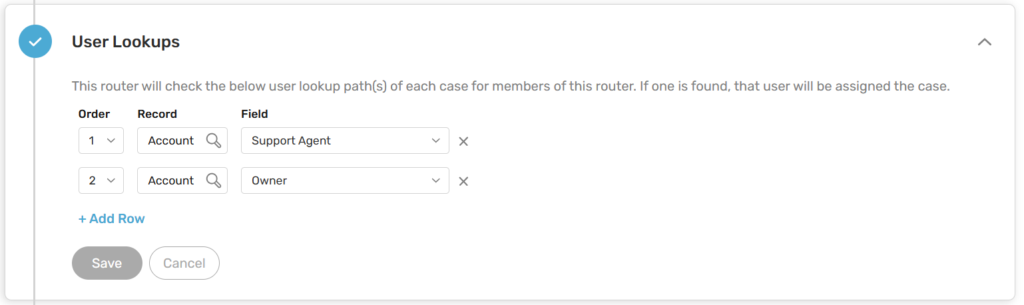
- Salesforce cases from the same account go to the support rep who handled previous cases
- Opportunities for related accounts go to the same sales rep
You select the matching field (email, company name, account lookup) and set timeframes (match against records from last 90 days, or look back further) to avoid perpetually assigning old accounts to reps who have moved on.
The rep who already knows the prospect can respond in under 5 minutes because they understand what was discussed, the prospect’s interests, and where the conversation left off.
A new rep needs to research everything from scratch, creating delays that kill conversion. Kubaru works across any Salesforce object (leads, contacts, accounts, cases, opportunities, custom objects) and provides detailed assignment logs showing exactly why each record was assigned, which duplicate rule triggered, and which existing record was matched.
Best For
Organizations with multiple lead sources where duplicates frequently enter through different channels. Large sales teams (100+ reps) where territory disputes over duplicates create friction. Companies with aggressive speed-to-lead goals who can’t afford delays from misrouted duplicates.
Limitations
Requires a Kubaru subscription at $20 per user per month. Needs properly configured Salesforce Duplicate Rules for Duplicate Matching Routers to work effectively (Assignment Matching works independently). Requires thoughtful configuration of matching fields and timeframes to avoid unintended routing.
4-Phase Process for Implementing Deduplication
Successful deduplication requires a structured approach rather than randomly implementing tools.
Phase 1: Define Requirements
Start by documenting your deduplication needs:
- List objects needing deduplication: Leads, contacts, accounts, opportunities, cases, custom objects?
- Identify matching fields for each object: Which fields uniquely identify records (email, phone, company name, account ID)?
- Specify matching methods: Exact match, fuzzy match, or custom logic for each field?
- Document business rules: When are intentional duplicates acceptable? How should conflicts be resolved?
- Quantify the problem: How many duplicates exist currently? How many new duplicates are created monthly?
Don’t skip this phase. Organizations that jump straight to tools without understanding their data end up with configurations that create more problems than they solve.
Phase 2: Choose Tools
Match your solution to organizational size, complexity, and budget:
- Small orgs (<5,000 records, <20 new records daily): Native Salesforce matching and duplicate rules plus manual merging
- Mid-market (5,000 to 50,000 records, 20 to 100 new records daily): Add third-party deduplication tool for automation
- Enterprise (>50,000 records, >100 new records daily): Full suite including third-party tools, preventive validation, and intelligent routing with territory management capabilities
Phase 3: Test in Sandbox
Never implement deduplication directly in production. Use a sandbox environment to:
- Configure matching rules and test against real data
- Review initial results for false positives (records incorrectly flagged as duplicates)
- Adjust matching criteria based on what you learn
- Test merge processes to ensure data preservation works correctly
- Validate that related records transfer properly
- Document edge cases and how to handle them
Run multiple test iterations until you’re confident the logic catches real duplicates without blocking legitimate records.
Phase 4: Implement and Monitor
Roll out gradually rather than flipping everything on at once:
- Start with one object (typically leads or contacts)
- Enable “alert” mode before “block” mode so you can monitor without breaking workflows
- Watch for false positives and adjust rules
- Communicate changes to users so they understand new workflows. For teams new to automated assignment, reviewing how Salesforce assignment rules work can help users understand the transition.
- Provide easy escalation path for users who encounter issues
Monitor key metrics during rollout:
- Duplicate detection rate
- False positive rate
- User complaints or workarounds
- Time to merge duplicates
- New duplicate creation rate
When evaluating your overall assignment strategy, consider reading our guide on the best Salesforce lead routing software to understand how duplicate handling fits into your broader routing needs.
Choose the Right Strategy Combination
No single strategy solves all duplicate problems.
Small teams can start with native Salesforce matching and duplicate rules. Mid-market organizations should add third-party deduplication tools for automation. Enterprise teams need the full suite: powerful deduplication tools, preventive validation, and intelligent duplicate routing to prevent duplicates from disrupting sales operations.
Ready to stop duplicate leads from disrupting your sales process? Try Kubaru free for 30 days and see how intelligent duplicate routing keeps your team focused on closing deals.



